Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMNFUZR)
| Drug Name |
Enalapril
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Vasotec; Enalapril (INN); Enalapril (TN); N-{(1S)-1-[(ethyloxy)carbonyl]-3-phenylpropyl}-L-alanyl-L-proline; N-[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]-L-alanyl-L-proline; (2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antihypertensive Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
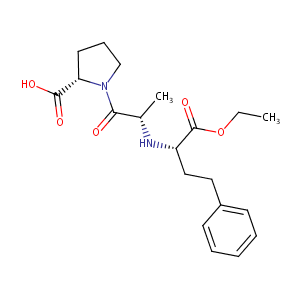 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 376.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Congestive heart failure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | BD10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Enalapril
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Enalapril (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Enalapril FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6322). | ||||
| 3 | Enalapril: a review of human pharmacology. Drugs. 1985;30 Suppl 1:13-24. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198500301-00004. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 6 | Ulm EH, Hichens M, Gomez HJ, Till AE, Hand E, Vassil TC, Biollaz J, Brunner HR, Schelling JL: Enalapril maleate and a lysine analogue (MK-521): disposition in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;14(3):357-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01991.x. | ||||
| 7 | Todd PA, Goa KL: Enalapril. A reappraisal of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in hypertension. Drugs. 1992 Mar;43(3):346-81. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199243030-00005. | ||||
| 8 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 9 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 10 | Determination of bezafibrate, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, orlistat and enalapril in waste and surface waters using on-line solid-phase extracti... J Environ Monit. 2009 Apr;11(4):830-8. | ||||
| 11 | Ethanol inhibits functional activity of the human intestinal dipeptide transporter hPepT1 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008 May;32(5):777-84. | ||||
| 12 | The intestinal H+/peptide symporter PEPT1: structure-affinity relationships. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2004 Jan;21(1):53-60. | ||||
| 13 | Vectorial transport of enalapril by Oatp1a1/Mrp2 and OATP1B1 and OATP1B3/MRP2 in rat and human livers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Jul;318(1):395-402. | ||||
| 14 | Uptake of enalapril and expression of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1 in zonal, isolated rat hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000 Jul;28(7):801-6. | ||||
| 15 | The modified dipeptide, enalapril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, is transported by the rat liver organic anion transport protein. Hepatology. 1998 Nov;28(5):1341-6. | ||||
| 16 | Summary of information on human CYP enzymes: human P450 metabolism data. Drug Metab Rev. 2002 Feb-May;34(1-2):83-448. | ||||
| 17 | Absorption and cleavage of enalapril, a carboxyl ester prodrug, in the rat intestine: in vitro, in situ intestinal perfusion and portal vein cannulation models. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2015 Sep;36(6):385-397. | ||||
| 18 | Characterization and kinetic analysis of enzyme-substrate recognition by three recombinant lactococcal PepVs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2006 Oct 15;454(2):137-45. | ||||
| 19 | Effects of enalapril maleate on blood pressure, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and peripheral sympathetic activity in essential hypertension. Clin Ther. 1987;9(4):390-9. | ||||
| 20 | Worsening of anemia by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and its prevention by antiestrogenic steroid in chronic hemodialysis patients. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 Suppl 3:S27-30. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900133-00007. | ||||
| 21 | Multichannel liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry cocktail method for comprehensive substrate characterization of multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 transporter. Pharm Res. 2007 Dec;24(12):2281-96. | ||||
| 22 | Captopril/enalapril inhibit promiscuous esterase activity of carbonic anhydrase at micromolar concentrations: An initro study. Chem Biol Interact. 2017 Mar 1;265:24-35. | ||||
| 23 | Effect of enalapril and losartan on cytokines in patients with stable angina pectoris awaiting coronary artery bypass grafting and their interaction with polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 gene. Am J Cardiol. 2004 Sep 1;94(5):564-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.05.017. | ||||
| 24 | The effect of early converting enzyme inhibition on neurohumoral activation in acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 1993 Nov;42(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(93)90100-u. | ||||
| 25 | A nonpeptide, piperidine renin inhibitor provides renal and cardiac protection in double-transgenic mice expressing human renin and angiotensinogen genes. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2008 Dec;22(6):469-78. doi: 10.1007/s10557-008-6131-x. Epub 2008 Aug 5. | ||||
| 26 | Health Canada "Potential risks of cardiovascular and renal adverse events in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with aliskiren (RASILEZ) or aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide (RASILEZ HCT)." . | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Diovan (valsartan). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Burnakis TG, Mioduch HJ "Combined therapy with captopril and potassium supplementation: a potential for hyperkalemia." Arch Intern Med 144 (1984): 2371-2. [PMID: 6391404] | ||||
| 29 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 30 | Mantyla R, Mannisto PT, Vuorela A, Sundberg S, Ottoila P "Impairment of captopril bioavailability by concomitant food and antacid intake." Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 22 (1984): 626-9. [PMID: 6389377] | ||||
| 31 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 32 | Asplund K, Wiholm BE, Lithner F "Glibenclamide-associated hypoglycaemia: a report on 57 cases." Diabetologia 24 (1983): 412-7. [PMID: 6411511] | ||||
| 33 | DeQuattro V "Comparison of benazepril and other antihypertensive agents alone and in combination with the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide." Clin Cardiol 14 (1991): iv28-32. [PMID: 1893639] | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 35 | Ban TA "Drug interactions with psychoactive drugs." Dis Nerv Syst 36 (1975): 164-6. [PMID: 1116424] | ||||
| 36 | Aronowitz JS, Chakos MH, Safferman AZ, Lieberman JA "Syncope associated with the combination of clozapine and enalapril." J Clin Psychopharmacol 14 (1994): 429-30. [PMID: 7884028] | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 38 | Warrington SJ, Ankier SI, Turner P "Evaluation of possible interactions between ethanol and trazodone or amitriptyline." Neuropsychobiology 15 (1986): 31-7. [PMID: 3725002] | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Yasmin (drospirenone-ethinyl estradiol) Berlex Laboratories, Richmond, CA. | ||||
| 40 | Katz RJ, Levy WS, Buff L, Wasserman AG "Prevention of nitrate tolerance with angiotension converting enzyme inhibitors." Circulation 83 (1991): 1271-7. [PMID: 1901528] | ||||
| 41 | Murphy BF, Whitworth JA, Kincaid-Smith P "Renal insufficiency with combinations of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and diuretics." Br Med J 288 (1984): 844-5. [PMID: 6322905] | ||||
| 42 | Baba T, Tomiyama T, Takebe K "Enhancement by an ACE inhibitor of first-dose hypotension caused by an alpha-blocker." N Engl J Med 322 (1990): 1237. [PMID: 1970122] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Inspra (eplerenone). Searle, Chicago, IL. | ||||
| 44 | Jarman PR, Mather HM "Diabetes may be independent risk factor for hyperkalaemia." BMJ 327 (2003): 812. [PMID: 14525902] | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 46 | Elsharkawy AM, Schwab U, McCarron B, et al. "Efavirenz induced acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation in a slow drug metaboliser." J Clin Virol 58 (2013): 331-3. [PMID: 23763943] | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. K-Dur (potassium chloride). Schering Laboratories, Kenilworth, NJ. | ||||
| 50 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 51 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Clolar (clofarabine). sanofi-aventis, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 54 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 55 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 56 | Perazella MA "Drug-induced hyperkalemia: old culprits and new offenders." Am J Med 109 (2000): 307-14. [PMID: 10996582] | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Clozaril (clozapine). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
